What is Bluetooth
Bluetooth is an open global standard for wireless data and voice communication. It is a special short-range wireless technology connection based on low-cost short-range wireless connection, which establishes communication environment for fixed and mobile devices. Originally created by Ericsson, it was later maintained and formulated by Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), a non-profit Bluetooth technology alliance.
Its name comes from Harald BlÃ¥tandï¼?Gormsen, the Nordic king who unified Denmark and Norway in the Middle Ages. It is named after the king’s surname “Blatand” and directly translated into Chinese as “Bluetooth” (BL = lan, tand = ya)., The Bluetooth logo  is a bind rune merging the Younger Futhark runes
is a bind rune merging the Younger Futhark runes (á?/strong>, Hagall) and
(á?/strong>, Bjarkan), Harald’s initials.
Specification
Frequency
Bluetooth operates at frequencies between 2.400 and 2.4835 GHz (ISM Band). and building personal area networks (PANs).
Channel
Bluetooth adopts 2.4GHz frequency band, with a channel every 2MHz, with a total of 40 physical channels. Before Bluetooth 5, in which there are 3 broadcast channels and 37 data channels. Starting from Bluetooth 5, the original three broadcast channels are named as Primary broadcast channels, and the remaining 37 channels are expanded into Secondary broadcast channels to improve the broadcast speed.
Because there are other wireless communication protocols in 2.4GHz band, such as WiFi and ZigBee, it is inevitable that there will be mutual signal interference in practical work, resulting in the degradation of data transmission quality. In order to cope with the interference, Bluetooth use a technique called Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH), that is, automatically avoiding the interfered radio frequency channel for communication.
Mode
Bluetooth technology is divided into two types: basic rate/enhanced data rate (BR/EDR) and low energy consumption (LE). Among them, BR/EDR type is one-to-one device communication created by point-to-point network topology; LE type uses a variety of network topologies such as point-to-point (one-to-one), broadcast (one-to-many) and grid (many-to-many)
Security
At present, Bluetooth has two security modes: LE security mode 1 and LE security mode 2. In addition, there are four security levels numbered from 1 to 4, of which 4 is the safest level. Therefore, when setting Bluetooth security mode, you can mix these two security modes.
https://www.bluetooth.com/bluetooth-resources/intro-to-bluetooth-security-part1/
https://www.bluetooth.com/bluetooth-resources/intro-to-bluetooth-security-part2/
Standards
Bluetooth technology was put forward in 1989, by Nils Rydbeck, CTO at Ericsson Mobile in Lund, Sweden, but the first official specification Bluetooth 1.0 was not officially announced by Bluetooth Special Interest Group until 1998. Since then, SIG has continuously introduced new specifications to improve Bluetooth technology. The most obvious point is that it has been greatly optimized and improved for Internet of Things applications since 4.0. The latest specification is Bluetooth 5.2 introduced in January 2020, which significantly improves the transmission distance and data transmission speed.
| Version | Year | Max transfer speed | Max range |
| bluetooth 5.2 | 2020 | 48 Mbit/s | 300 meters |
| bluetooth 5.1 | 2019 | 48 Mbit/s | 300 meters |
| bluetooth 5 | 2016 | 48 Mbit/s | 300 meters |
| bluetooth 4.2 | 2014 | 24 Mbit/s | 50 meters |
| bluetooth 4.1 | 2013 | 24 Mbit/s | 50 meters |
| bluetooth 4.0 | 2010 | 24 Mbit/s | 50 meters |
| bluetooth 3.0+HS | 2009 | 24 Mbit/s | 10 meters |
| bluetooth 2.1+EDR | 2007 | 3 Mbit/s | 10 meters |
| bluetooth 2.0+EDR | 2004 | 2.1 Mbit/s | 10 meters |
| bluetooth 1.2 | 2003 | 1 Mbit/s | 10 meters |
| bluetooth 1.1 | 2002 | 810 Kbit/s | 10 meters |
| bluetooth 1.0 | 1998 | 723.1 Kbit/s | 10 meters |
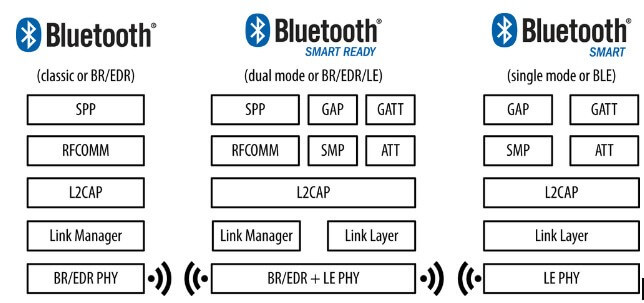
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
With the development of IOT, BLE is more and more widely used in mobile devices and smart devices
BLE is one of the subsets of Bluetooth 4.0, which is designed to reduce energy consumption, keep the communication range/speed similar to that of classic Bluetooth, and be better applied to devices powered by coin batteries, such as sensors, so that it can last for months or years.
| technical/technological specification | Classic Bluetooth | BLE |
| Radio Frequency | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | 10 meter/100 meter | 30 meters |
| Speed | 1-3 Mb/s | 1 Mb/s |
| Act Speed | 0.7-2.1 Mb/s | 0.2 Mb/s |
| nodeï¼unit | 7-16,777,184 | Undefined (theoretical maximum is 2^32) |
| Security | 64/128-bit and user-defined application layer | 128-bit AES and user-defined application layer |
| Robustness | Automatic adaptive fast frequency hopping, FEC, fast ACK | Automatic adaptive fast frequency hopping |
| Latencyï¼Unconnected stateï¼?/td> | 100 ms | <6 ms |
| Total time to send data | 0.625 ms | 3 ms |
| Audio | yes | LE audio https://www.bluetooth.com/learn-about-bluetooth/bluetooth-technology/le-audio/ https://www.bluetooth.com/media/le-audio/le-audio-faqs/ |
| network topology | (Distributed Networks) | ï¼Star topologyï¼?nbsp;ï¼Bus topologyï¼?nbsp;ï¼Mesh topologyï¼?/td> |
| Power consume | 1ï¼As a referenceï¼?/td> | 0.01to 0.5ï¼Depending on the usageï¼?/td> |
| Maximum operating current | <30 mA | <15 mAï¼The maximum operating time is 15 mA ï¼?/td> |
| main application | Mobile phones, game consoles, headphones, stereo audio streams, cars and PCs, etc. | Mobile phones, game machines, PCs, watches, sports and fitness, health care, automobiles, home electronics, automation and industry, etc. |
BLE has two different types of devices.
Bluetooth Smart Ready-This is a central device, which is powered by batteries and has high resources and can run all Bluetooth protocols. They are your laptop and mobile phone.
Bluetooth smart-they are your terminal devices, like fitness trackers, baggage trackers or smart dildos. They don’t need to run the whole stack, they need to save power and resources. They only run bluetooth LE servers. They are peripheral devices to which the central device can be connected.
Bluetooth Qualification
Every bluetooth product needs to be certified according to the bluetooth SIG certification and declaration process. Products need to meet the requirements of Bluetooth license agreement and specification
The qualified products would have a QDID and listed on the Bluetooth Product Listing Database.
Resources
Bluetooth SIG Official website
Bluetooth on Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bluetooth
Understanding Bluetooth Technology | CISA
http://news.eeworld.com.cn/mp/BLE5CODER/a88067.jspx
Youtube Channel