[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”3.0.47″][et_pb_row _builder_version=”3.0.48″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”3.0.47″ parallax=”off” parallax_method=”on”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.6″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”]
Your WiFi signal is not able to reach your bedroom? A lot of people are suffering from an unstable and weak WiFi signal in their homes. By using a WiFi extender, you can increase the strength of your WiFi signal and extend the range of your network.
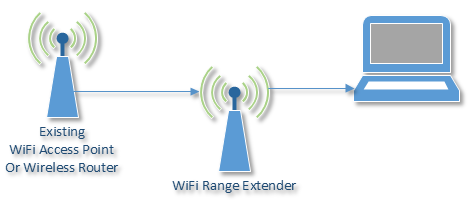
What Is a WiFi Extender?
WiFi extender, also known as repeaters, connect to your WiFi and repeat/duplicate the signal to extend the coverage within a certain area. They can help reach behind signal-blocking walls or simply transmit the signal further when positioned right.
As long as the specs of the WiFi router match the extenderâs, they will work. Also, you will probably have to configure the extender to connect to your WiFi.
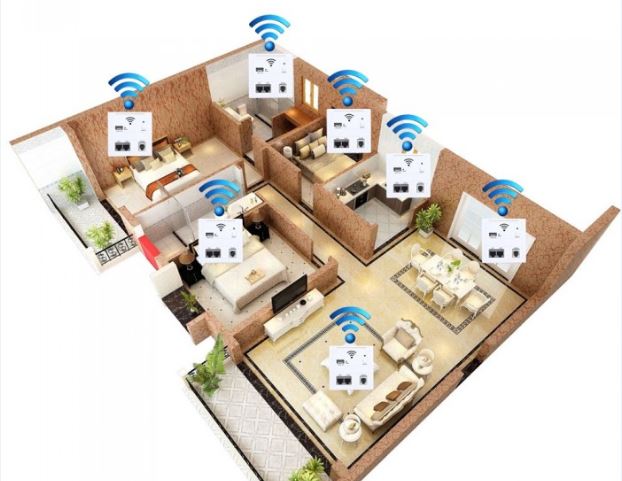
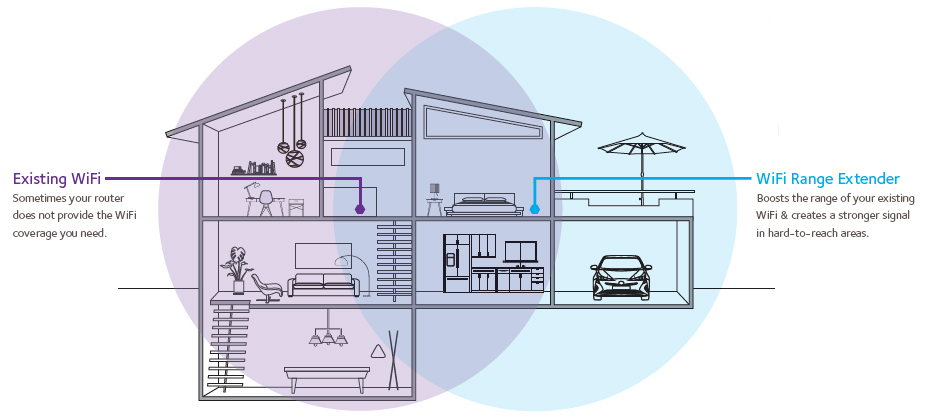
How a WiFi Extender Works
A WiFi repeater has two wireless routers, like the WiFi router you have in your office or home. One of them act like receiver to picks up the already existing WiFi network, it will then transfer the signal to the second WiFi router – sender, and the sender will transmit the boosted signal for all devices to pick it up. Usually people will use one router and multi-extender to extend the WiFi coverage area and the network topology just look like star, the router at the center and extenders around it.
WiFi Extender Pros and Cons
Pros
- Good for small houses
- Less expensive than other WiFi systems
- You can keep using your existing router
Cons
- Somewhat difficult to configure
- Not very smooth for house usage
Things You Need to Consider
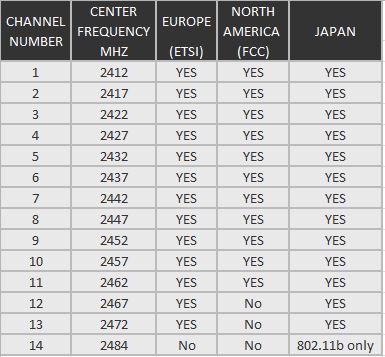
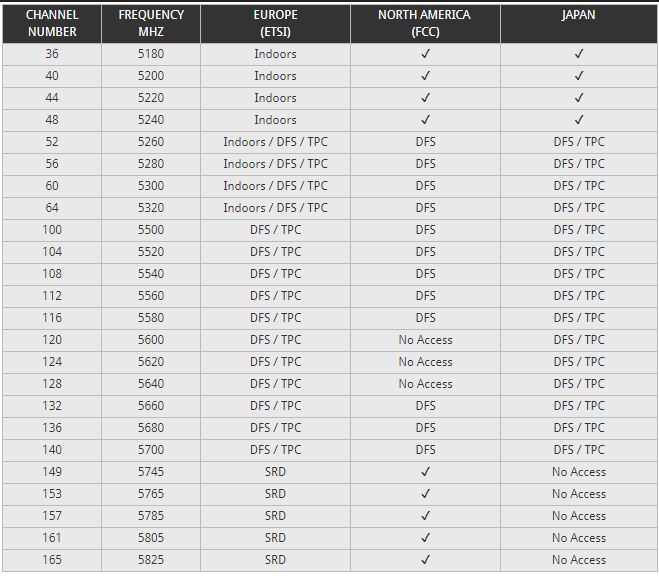
Number of Channels
Nowadays, many of the WiFi extender work with both 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz radio frequencies, but itâs possible that some of them arenât compatible with your existing router.
2.4 GHz WiFi channels & frequencies
5 GHz WiFi channels & frequencies
Wired LAN Ports
If you want to use a WiFi extender to connect other wired devices, such as a smart TV or desktop computer, with a plan to get a better WiFi connection, then you should keep in mind the number of wired LAN ports you have. We think that itâs good to have some extra LAN ports for the future use.
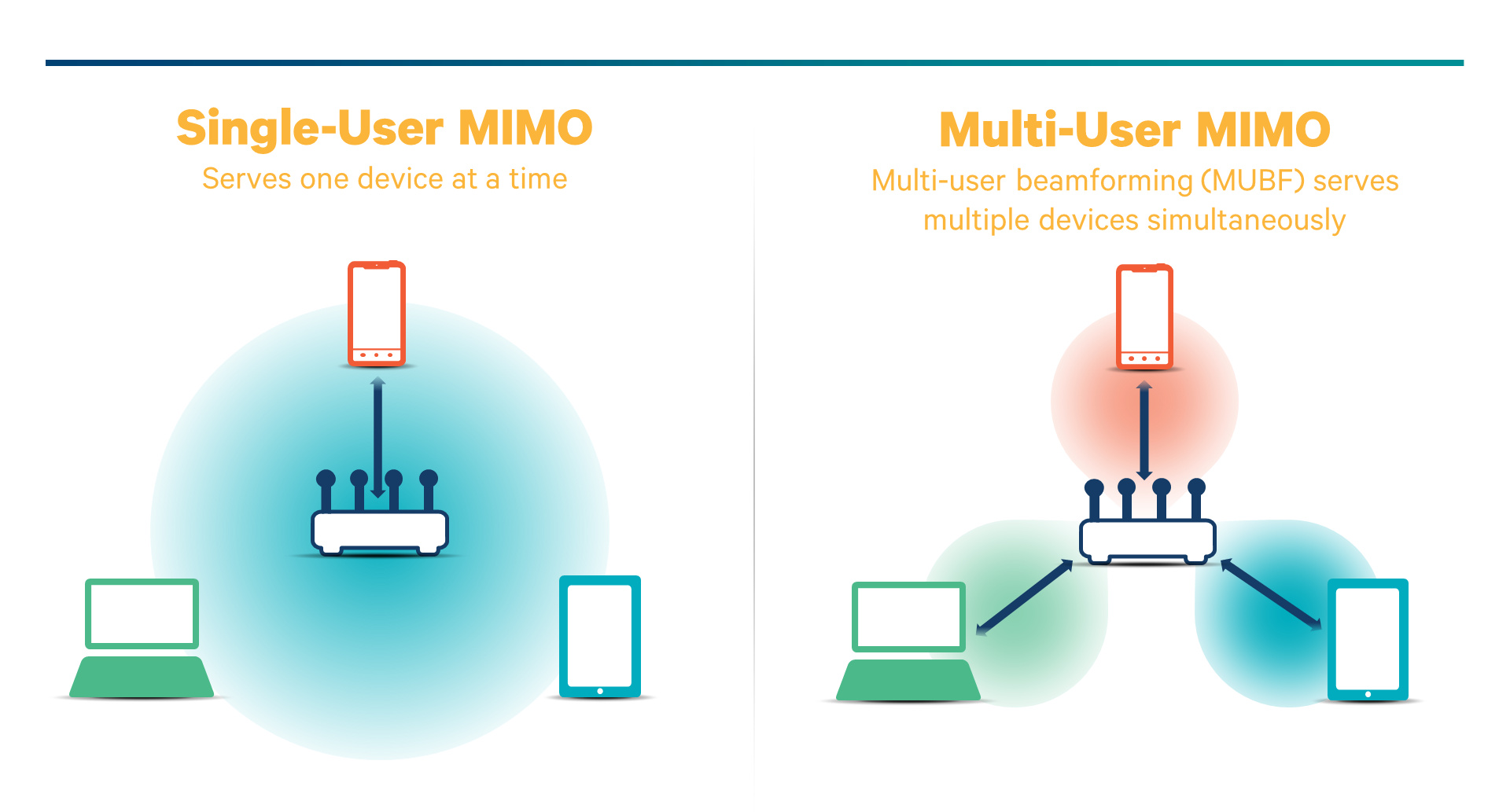
MU-MIMO
You can use MU-MIMO (multi-user, multiple inputs, multiple outputs) to support environments where multiple users are trying to access a wireless network at the same time. If your router has the ability, then we highly recommend choosing an MU-MIMO-supported WiFi extender.
Security & Encryption
The security protocol is one thing we easy to ignore. Why is the acronym for your security protocol important? As with all security measures, the increasing the power of computers and known vulnerabilities are putting old WiFi standards at huge risk. Itâs your data and network, and if someone tries to attack you for illegal purposes, the police are going to knock on your door. You should try to understand all of the security protocols well enough to implement the latest one that your router supports. Doing so will help you block access to your home network.

Wired Equivalent Privacy
Wired Equivalent Privacy, better known as WEP, is the most popular WiFi security protocol. Most people reading this are probably using it. This is because itâs the oldest, is backward compatible, and is usually listed first in the menus for the protocol selection of router panels.

In the fall of 1999, The WiFi Alliance confirmed WEP as a WiFi network security standard. WEPâs first versions werenât very strong, though, even for 1999. This is because of the United Statesâ?restrictions on exports of numerous cryptographic technologies, which caused the manufacturers to restrict the capability of their devices. However, these companies were able to build higher security devices once the U.S. lifted the restrictions.
Still, theyâre not perfect, and as the power of computers increased, people were easily able to crack WEP security. The FBI demonstrated to the public why WEP is a very insecure system in 2005. They used free software and cracked numerous WEP passwords in only a few minutes.
Even with the many workarounds, numerous improvements, and other efforts to make WEP usable, it is still very vulnerable. People who use WEP really should upgrade their security, or if this is not an option on your existing router, replace it. The WiFi Alliance retired WEP in 2004 officially.
WiFi (WPA) Protected Access
WiFi Protected Access, better known as WPA, was the WiFi Allianceâs replacement for WEP. They formally accepted it in 2003, only a year before they stopped recommending WEP. WPA systems are much more secure than WEP.

WPAs can also detect when someone is trying to interfere with them. Still, WPAs used parts recycled from WEP systems, and hackers soon learned how to exploit those weak components in the system.
WPA, the same as the WPE system, has been shown to be an inadequate security measure against attacks. The interesting thing is that the process by which hackers usually break into WPA is usually not a direct hack on the WPA but through an alternative system that was put out with WPA â?WiFi Protected Setup. This secondary system was designed to enable devices to link together within the network.
WiFi (WPA2) Protected Access 2
As of 2006, WPA2 significantly suppressed WPA. At the moment, the main security threat to the WPA2 system is an indirect one. It requires that the attacker have access to the secured WiFi network to gain access to important keys and then continue an attack against all devices connected to the network. Because this is the case, the security weaknesses are limited nearly entirely to industry level networks and shouldnât be a concern for users at home.

Unfortunately, the same threat that is the largest hole in the armor of WPA â?the route of attack through the WiFi Protected Setup (used for connecting different devices) â?is still present in modern WPA2 access points. The bright side is that breaking into a WPA or WPA2 secured network using this hacking method requires anywhere from two to fourteen hours of constant effort with a modern computer. Most attackers wonât even bother wasting that much time to access a home network.
Still, it is still a legitimate security concern. To ensure that you are using the highest level of security, you should disable WPS entirely, and, if possible, you should flash the firmware of the access point to a distribution that doesnât even support WPS. Doing so will remove the threat of someone breaking into your network through the WPS.
WiFi Security Knowledge Acquired; What Now?
You are now probably feeling very confident since you are using the best security protocol that you can for your WiFi. Or are you? Maybe you are nervous because you are still using WEP security for your WiFi access point because it was listed first on your router? If this is the case, donât worry. We have you covered.
![]()
Here is something you should know before you keep on reading our other articles on WiFi security. This list represents security methods regarding WiFi, and they are available on all modern routers.
- WPA + AES
- WPA2 + AES
- WPA + TKIP
- WPA + TKIP AES
- WEP
- Open Network
In a best-case scenario, you are going to disable WiFi Protected Setup and set your router to WPA2 + AES. Everything else on this list is second-best if not worse. For example, if you choose to go with WEP, your level of security will be so low that youâre practically inviting anyone into your WiFi network. It represents a fence at best. This fence marks the perimeter of your property, but everyone knows that they can climb over it if they want to. And you might not know that they did until itâs too late.
But now that you have some basic understanding of how the security of WiFi works and how you can upgrade and further enhance your home network, thereâs no reason that you canât have a very secure WiFi network.
Statistics on Hackers
According to recent reports, every 39 seconds a hacker attacks someone. Evidence shows that 43% of these attacks are targeting small businesses.

Healthcare is also not safe. Statistics show that over 75% of the industry was affected by malware in 2016 alone. With security in industries getting stronger against attacks, itâs likely that hackers will turn their attention to home networks where they can easily access your financial accounts or other personal data.

Desktop or Plug-In
You will find two types of WiFi extender: plug-in and desktop. Usually, desktop extenders will look like your traditional WiFi router. They have adjustable antennas on the exterior, USB ports for peripherals, and a couple of LAN ports so that you can connect your devices (gaming consoles, TVs, etc.).

Plug-in extenders are a bit different than desktop units. They are much smaller, and you have to insert them directly into a wall. A couple of models have antennas on the exterior, while other models have them on the inside to present an even safer option. Considering their size, these extenders will usually have only one LAN port, and they donât have USB connectivity options. This makes them much more affordable, but with much less versatility. If you donât want to sacrifice a wall outlet, check for plug-in models with a pass-through for other power cords.

Disclosure
Donât be so hasty to trash your old router. By adding a WiFi extender in your home, you might also resolve most of weak WiFi signal issues. Itâs a compromise compared to a Mesh network whole-home solution, but it works in most cases meanwhile you save a lot of money.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]